
Integrate SonarQube into Pipelines
SonarQube is a mainstream tool for continuous inspection of code quality, which can be used for static and dynamic analysis of code repositories. After SonarQube is integrated into pipelines, common code issues detected in running pipelines, such as bugs, will be displayed directly on the dashboard.
This document demonstrates how to integrate SonarQube into pipelines. Before creating a pipeline using a Jenkinsfile, please read this document.
Prerequisites
DevOps must have been installed and enabled.
Install SonarQube Server
To integrate SonarQube into your pipeline, you must first install the SonarQube server on your cluster nodes.
-
Install Helm to use it to install SonarQube. For example, run the following command to install Helm 3:
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/scripts/get-helm-3|bashView the Helm version.
helm version version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.4.1", GitCommit:"c4e74854886b2efe3321e185578e6db9be0a6e29", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.14.11"}Note For more information, see the Helm Documentation.
-
Run the following command to install the SonarQube server.
helm upgrade --install sonarqube sonarqube --repo https://charts.kubesphere.io/main -n \ kubesphere-devops-system --create-namespace --set service.type=NodePortNote Ensure that you use Helm 3 to install the SonarQube server.
Get SonarQube Console Address
-
Run the following command to get the SonarQube NodePort.
export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace kubesphere-devops-system -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services sonarqube-sonarqube) export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace kubesphere-devops-system -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}") echo http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORT -
Expected output: (Your NodeIP and NodePort should be different)
http://10.77.1.201:31377
Configure SonarQube Server
Step 1: Access SonarQube Console
-
Run the following command to check the status of SonarQube. Note that you can only access the SonarQube console after SonarQube is running.
$ kubectl get pod -n kubesphere-devops-system NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE devops-jenkins-68b8949bb-7zwg4 1/1 Running 0 84m sonarqube-postgresql-0 1/1 Running 0 5m31s sonarqube-sonarqube-bb595d88b-97594 1/1 Running 2 5m31s -
Access the SonarQube console http://NodeIP:NodePort in your browser.
-
Click Log in in the upper-right corner and log in with the default account admin/admin.
Note Depending on where the instance is deployed, you may need to set the necessary port forwarding rules and allow the port in your security group to access SonarQube.
Step 2: Create SonarQube Admin Token
-
Click the letter A in the upper-right corner, then select My Account from the menu to go to the Profile page.
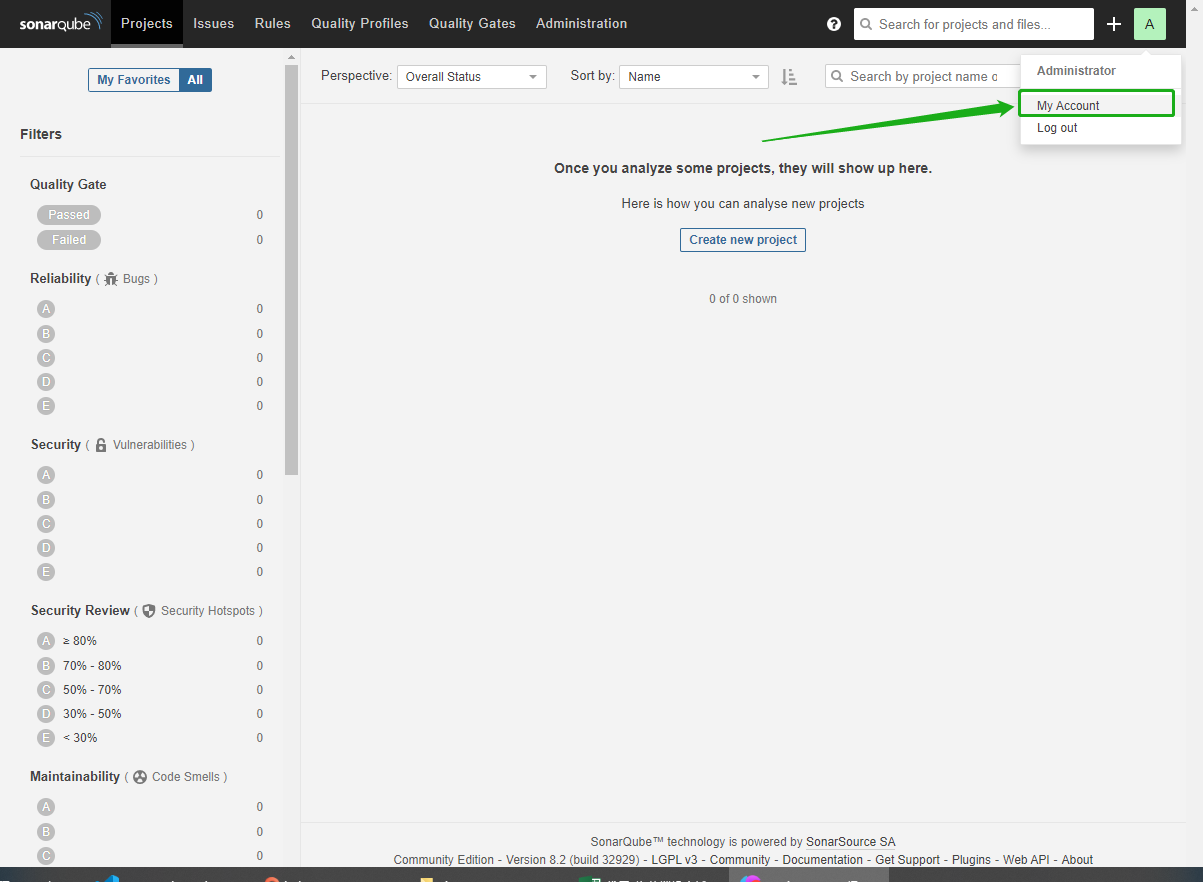
-
Click Security and enter a token name, for example, kubesphere.
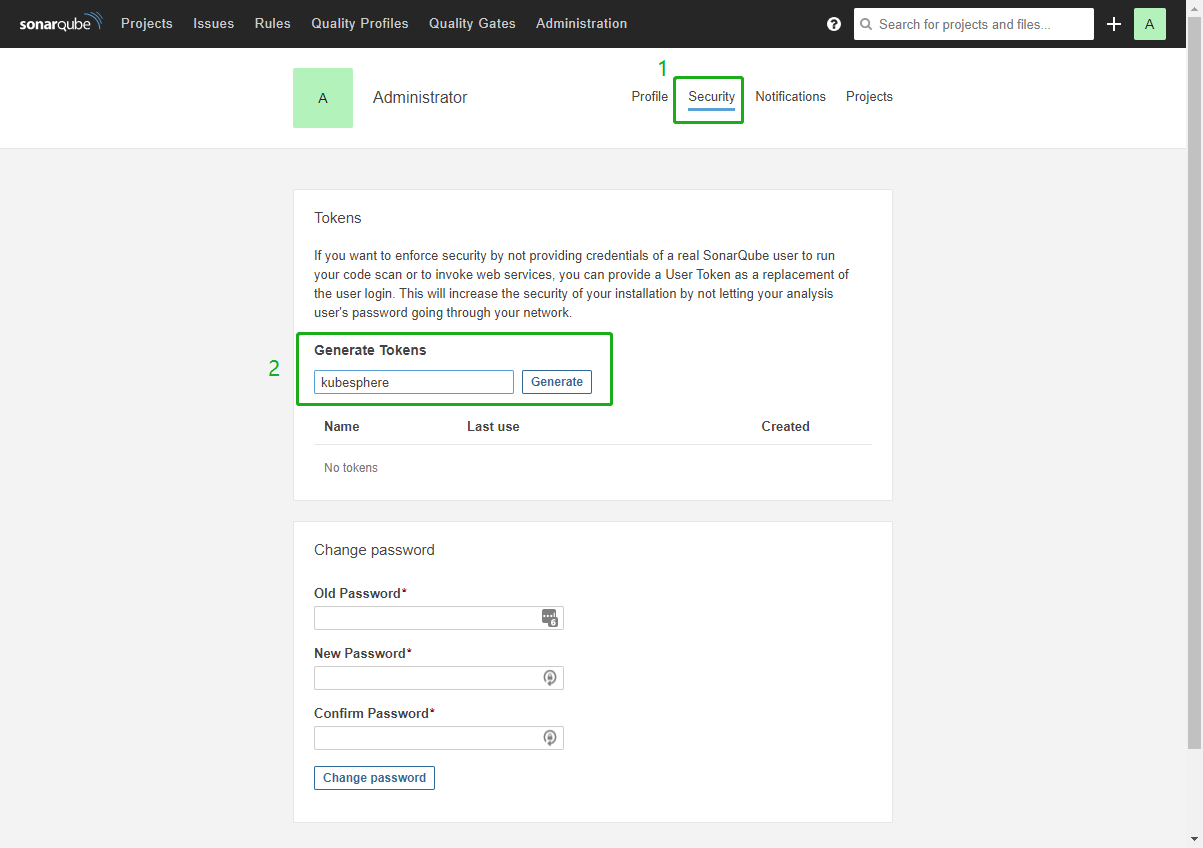
-
Click Generate and copy this token.
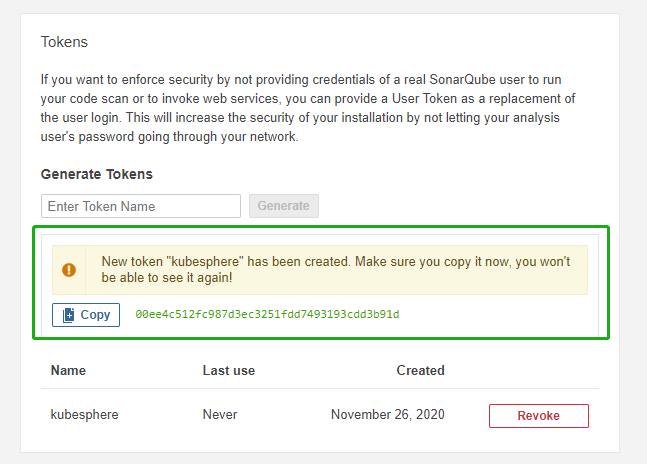
Note As indicated, you cannot view this token again, so make sure you copy it successfully.
Step 3: Create Webhook Server
-
Run the following command to get the address of the SonarQube Webhook.
export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace kubesphere-devops-system -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services devops-jenkins) export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace kubesphere-devops-system -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}") echo http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORT/sonarqube-webhook/ -
Expected output:
http://10.77.1.201:30180/sonarqube-webhook/ -
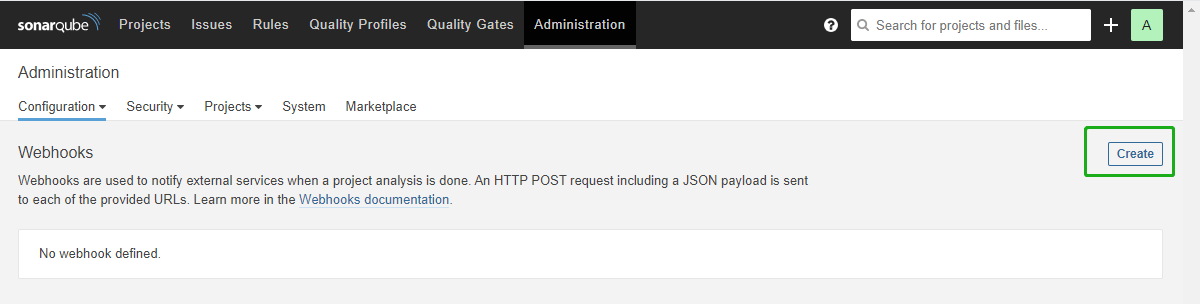
Click Administration, Configuration, and Webhooks to create a Webhook.
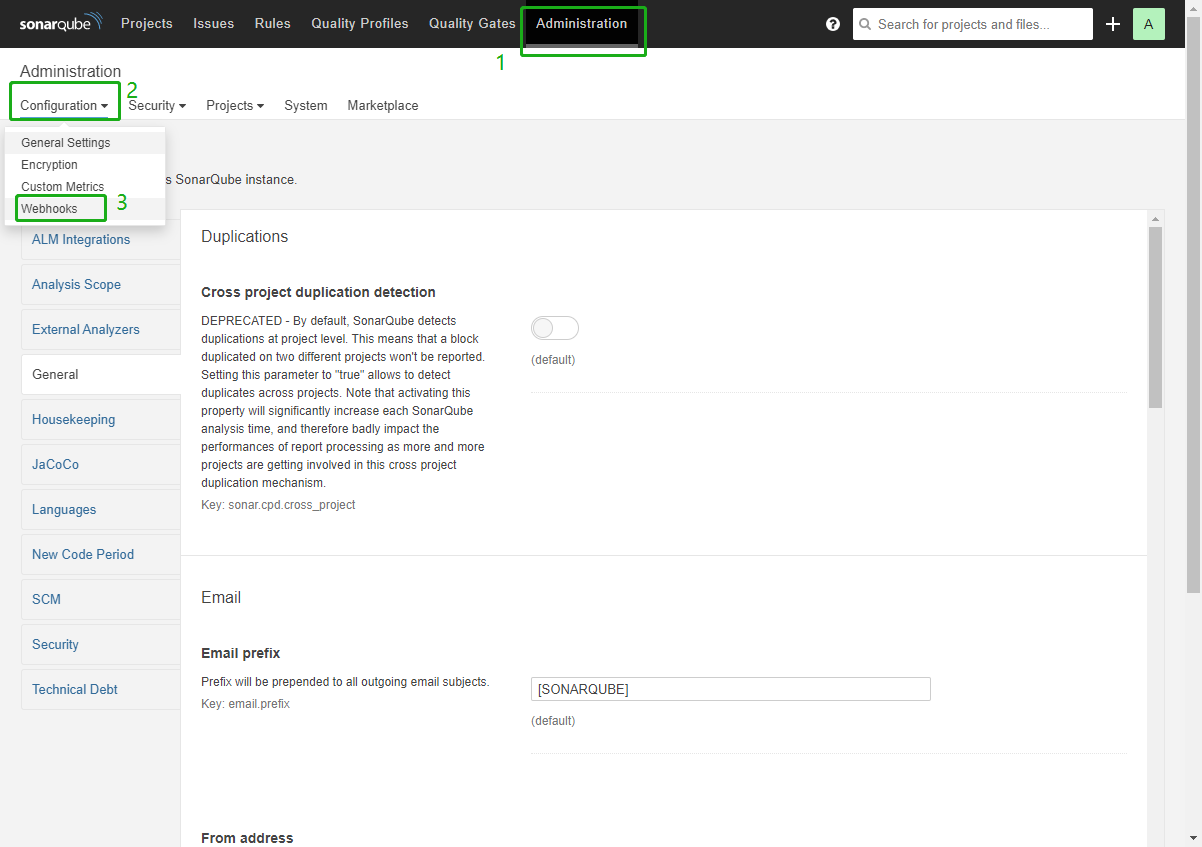
-
Click Create.
-
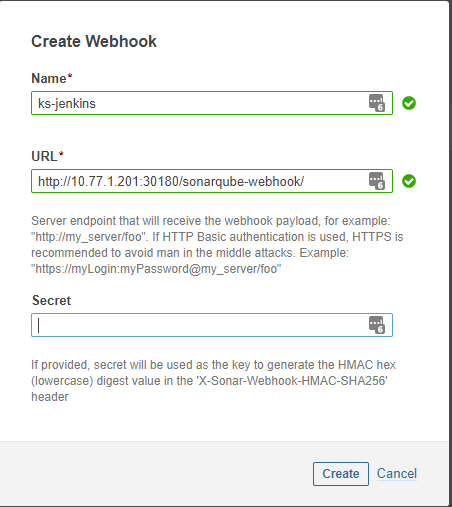
In the dialog box that appears, enter Name and Jenkins Console URL (i.e., the SonarQube Webhook address). Click Create to complete the operation.
Step 4: Add SonarQube Server to Jenkins
-
Run the following command to get the address of Jenkins.
export NODE_PORT=$(kubectl get --namespace kubesphere-devops-system -o jsonpath="{.spec.ports[0].nodePort}" services devops-jenkins) export NODE_IP=$(kubectl get nodes --namespace kubesphere-devops-system -o jsonpath="{.items[0].status.addresses[0].address}") echo http://$NODE_IP:$NODE_PORTYou will get the following output:
http://10.77.1.201:30180 -
Refer to Access Jenkins dashboard for configuration.
-
Access Jenkins using the address http://NodeIP:30180.
The Jenkins dashboard is installed by default when DevOps is installed. Additionally, Jenkins is configured with KubeSphere LDAP, meaning you can log in to Jenkins directly using your KubeSphere account (e.g.,
admin/P@88w0rd). For more information on configuring Jenkins, see Jenkins System Settings.Note Depending on where the instance is deployed, you may need to set the necessary port forwarding rules and allow port 30180 in your security group to access Jenkins.
-
Click Manage Jenkins in the left navigation pane.
-
Scroll down and click Configure System.
-
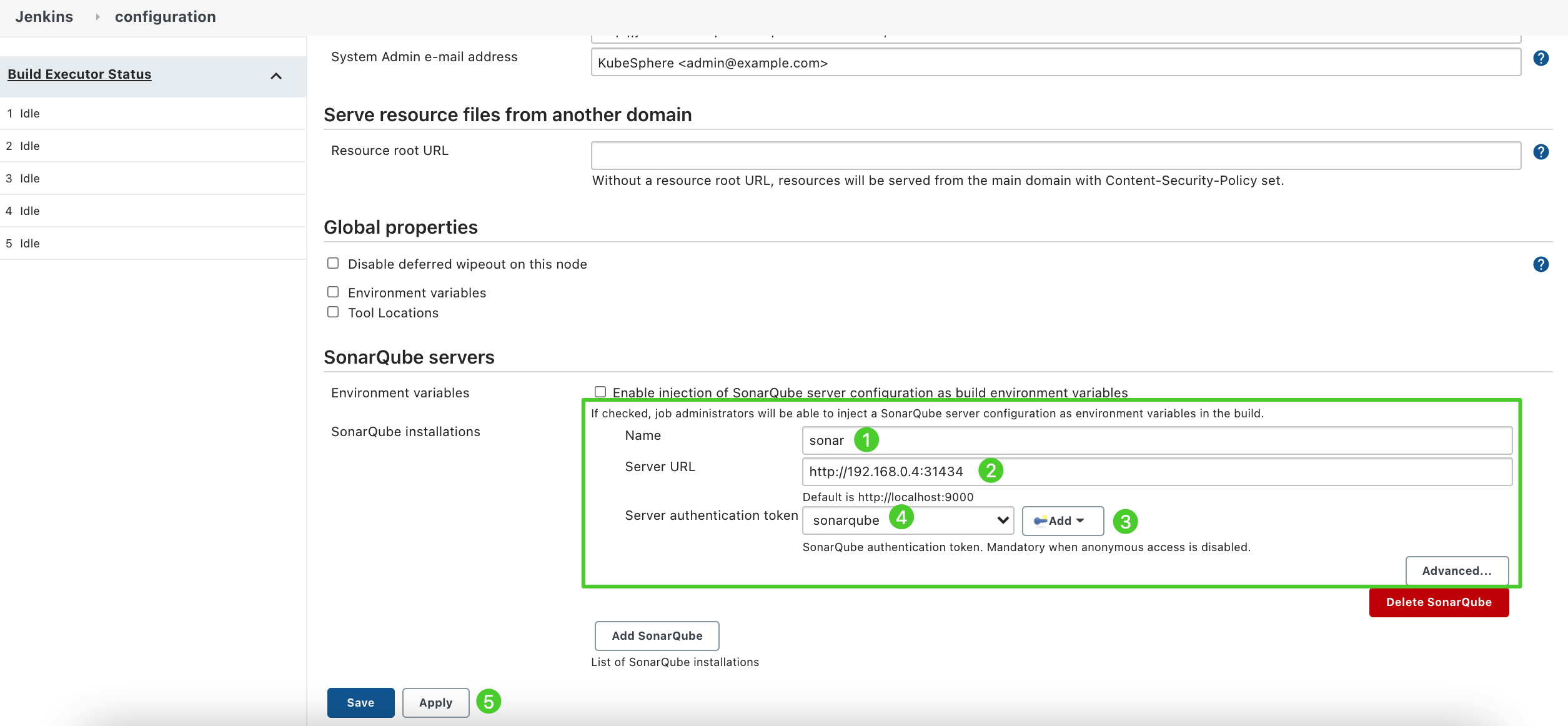
Search for SonarQube servers and click Add SonarQube.
-
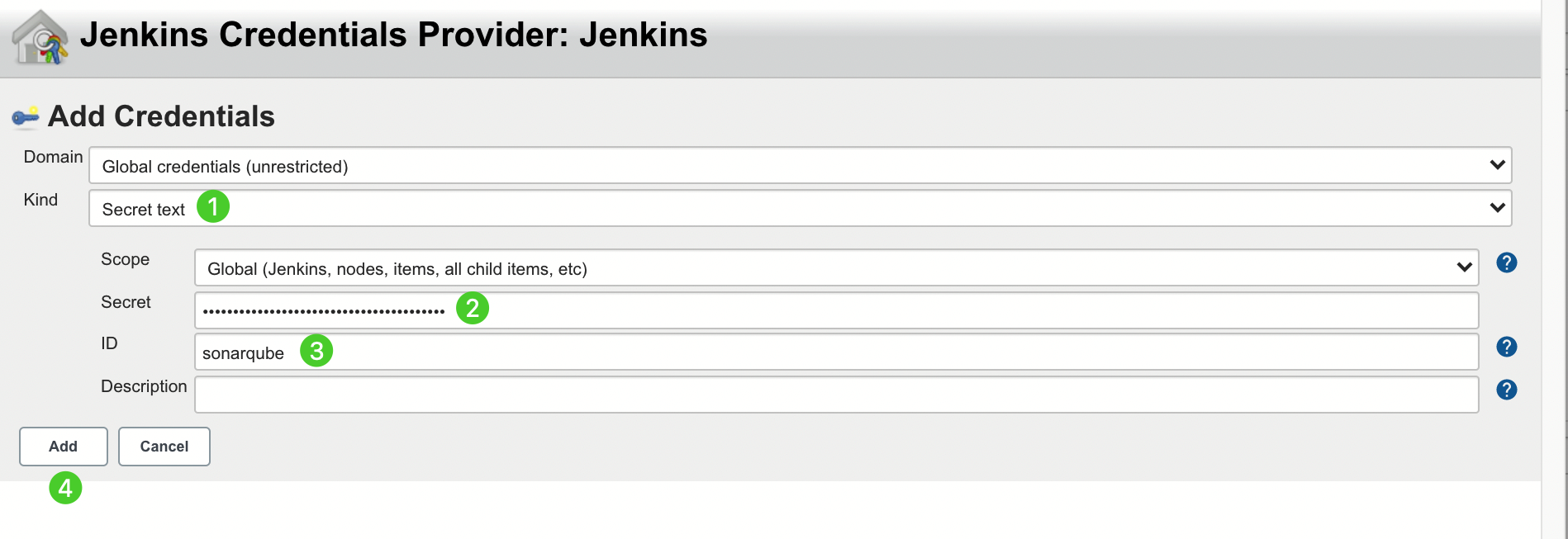
Enter Name and Server URL (http://NodeIP:NodePort). Click Add, select Jenkins, and create credentials with the SonarQube admin token in the dialog box that appears (as shown in the second screenshot below). After creating the credentials, select them from the dropdown list next to Server authentication token. Click Apply to complete the operation.
Note If the Add button does not work, go to Manage Jenkins > Manage Credentials and click Jenkins under Stores scoped to Jenkins. Click Global credentials (unrestricted) and then click Add Credentials in the left navigation pane. Add credentials with the SonarQube admin token as shown in the second screenshot below. After adding the credentials, select them from the dropdown list next to Server authentication token.
Step 5: Add SonarQube Configuration to DevOps
-
Run the following command to edit the ConfigMap
devops-config.kubectl -n kubesphere-devops-system edit cm devops-config -
Add the field
sonarQubeafter thedevopssection and specifyhostandtokenunder it.devops: host: http://devops-jenkins.kubesphere-devops-system username: admin maxConnections: 100 namespace: kubesphere-devops-system workerNamespace: kubesphere-devops-worker sonarQube: host: http://10.77.1.201:31377 token: 00ee4c512fc987d3ec3251fdd7493193cdd3b91d -
Save this file.
Step 6: Add sonarqubeURL to KubeSphere Console
You need to specify sonarqubeURL so that you can access SonarQube directly from the KubeSphere web console.
-
Run the following command:
kubectl edit cm -n kubesphere-system ks-console-config -
Search for data:client:enableKubeConfig and add the devops field below it, specifying sonarqubeURL.
client: enableKubeConfig: true devops: # Add this field manually. sonarqubeURL: http://10.77.1.201:31377 # SonarQube IP address. -
Save the file.
Step 7: Restart Services
Run the following commands to restart the services.
kubectl -n kubesphere-devops-system rollout restart deploy devops-apiserver
kubectl -n kubesphere-system rollout restart deploy ks-console
Create a SonarQube Token for the New Project
Create a SonarQube token so that the pipeline can communicate with SonarQube when running.
-
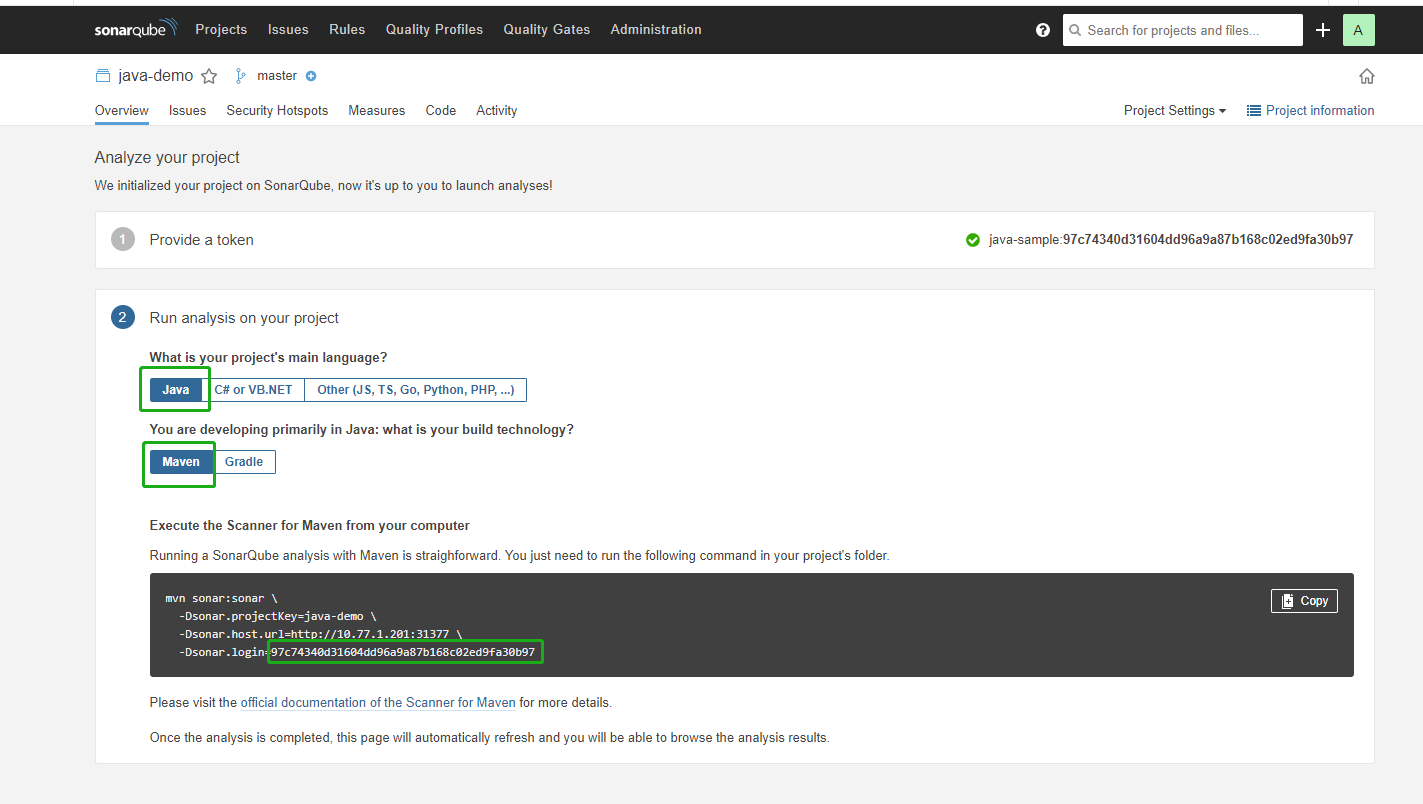
On the SonarQube console, click Create new project.
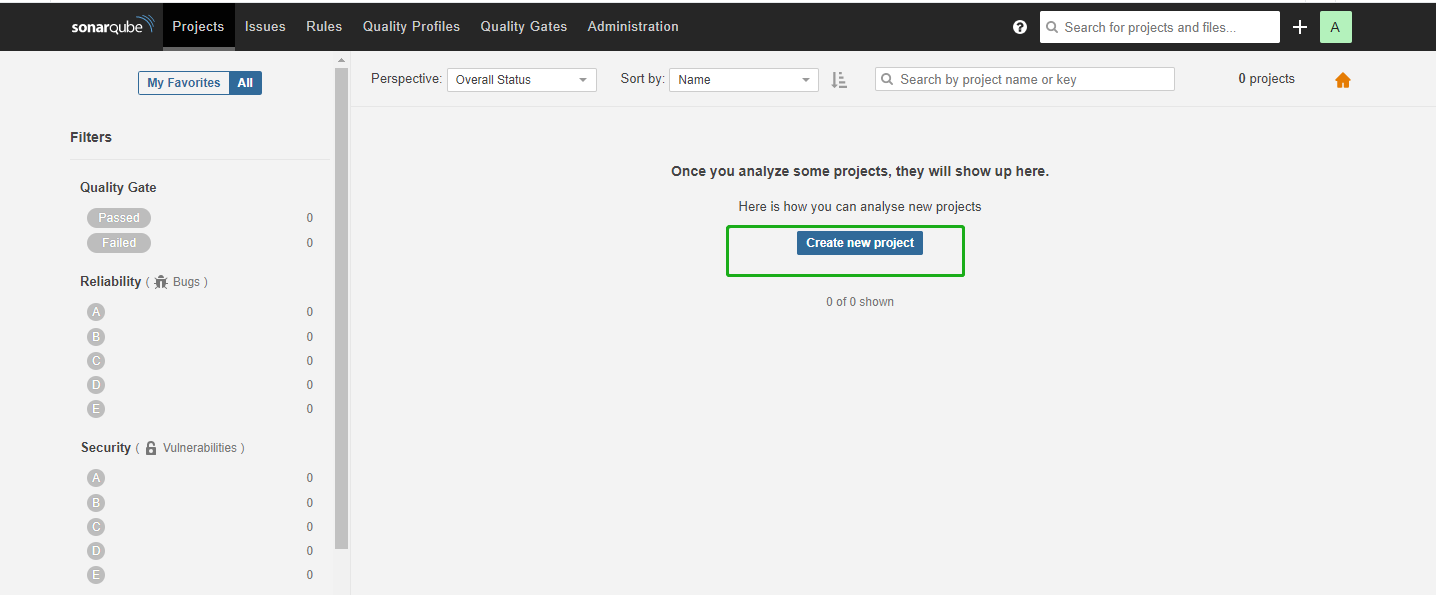
-
Enter a project key, for example, java-demo, and click Set Up.
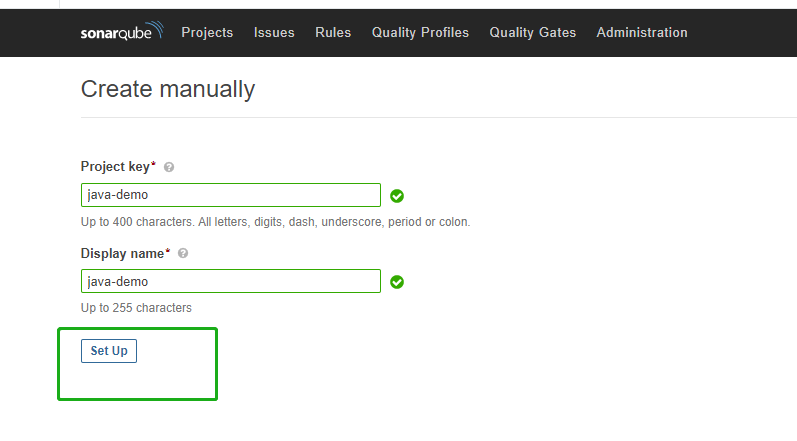
-
Enter a project name, for example, java-sample, and click Generate.
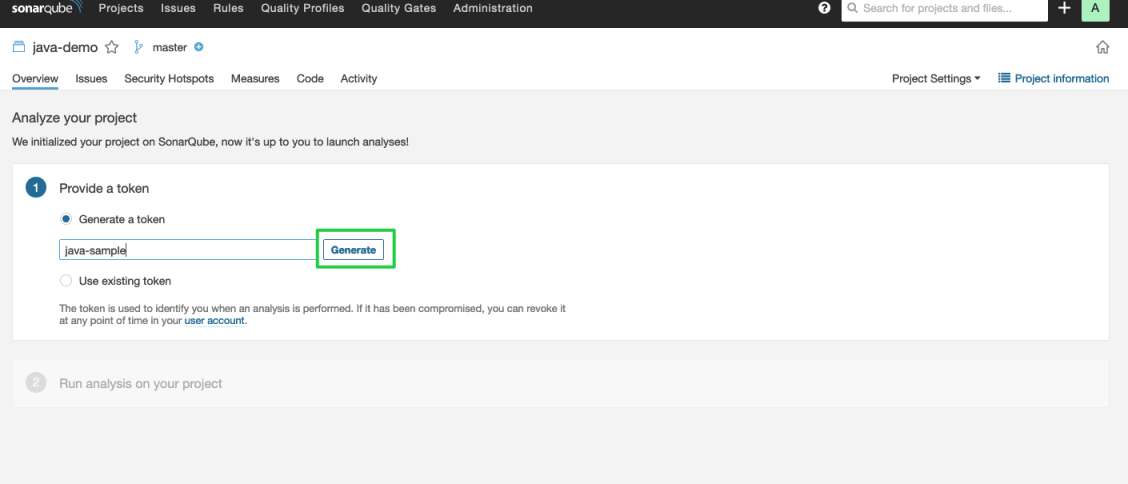
-
After creating the token, click Continue.
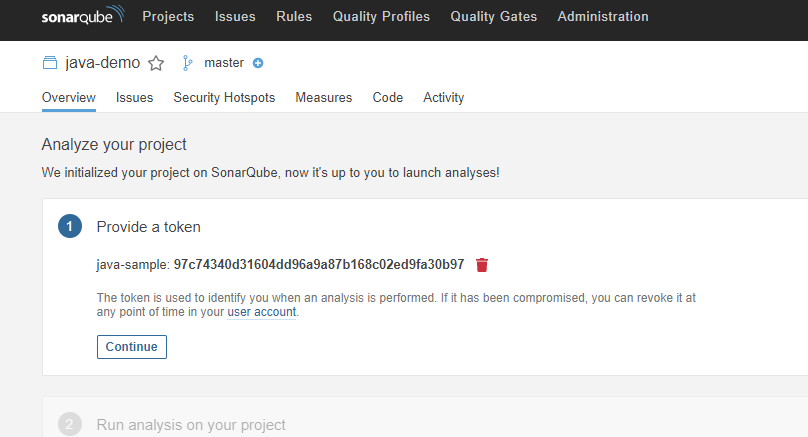
-
Select Maven and copy the sequence number in the green box shown in the figure below. If you want to use it in the pipeline, you need to add this sequence number in credentials.
View Results in KubeSphere Console
After creating a pipeline using a Jenkinsfile or creating a pipeline using graphical editing panels, you can view the results of code quality analysis.
Feedback
Was this page Helpful?
Receive the latest news, articles and updates from KubeSphere












 Previous
Previous
